Botox injections, Procedure, Benefits, Risks
Botox injections, Procedure, Benefits, Risks
Botox injections are the best known of a group of medications that use various forms of botulinum toxin to temporarily paralyze muscle activity to stop ageing.
This toxin is produced by the microbe that causes botulism, a type of food poisoning.
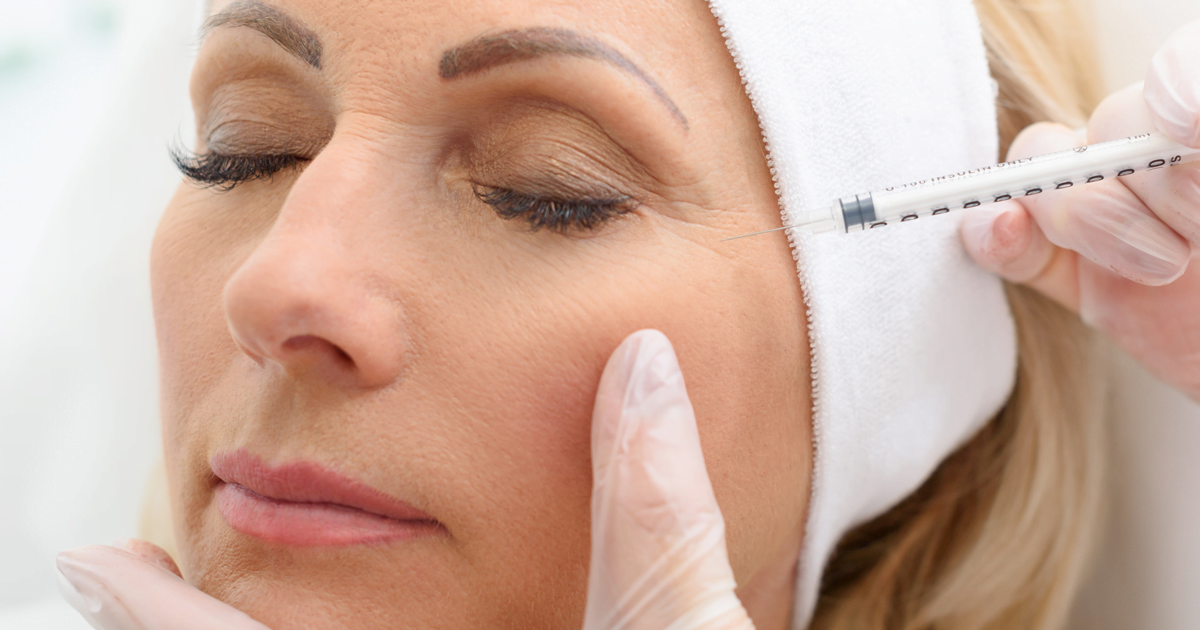
Botox injections are noted primarily for the ability to reduce the appearance of some facial wrinkles and fine lines.
They are also used to treat such problems as repetitive neck spasms (cervical dystonia), excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis), overactive bladder and the lazy eye.
Botox injections may also help prevent chronic migraines in some people. Botox was the first drug to use botulinum toxin. Other products now include Dysport, Myobloc and Xeomin drugs.
Each is a little different, particularly when it comes to dosage units, so they are not interchangeable.
Why it’s done:
Botulinum toxin injections or botox block certain chemical signals from nerves, mostly signals that cause muscles to contract.
The most common use of these injections is to temporarily relax the facial muscles that underlie and cause wrinkles and fine lines, such as:
- Frown lines between the eyebrows.
- Crow’s-feet, the lines that fan out from the corners of the eyes.
- Forehead furrows.
Botulinum toxin injections are also used to treat conditions that affect how the body functions. Examples include:
Cervical Dystonia: In this painful condition, Your neck muscles contract involuntarily causing your head to twist or turn into an uncomfortable position.
Lazy eye: The most common cause of lazy eye is an imbalance in the muscles responsible for positioning the eye.
Muscle contractures: Some neurological conditions, Such as cerebral palsy, can cause your limbs to pull in toward your centre.
In some cases, these contracted muscles can be relaxed with botulinum toxin injections.
Hyperhidrosis: In this condition, Excessive sweating occurs even when the temperature isn’t hot and you’re not exerting yourself.
A chronic migraine: If you experience migraines more than 15 days a month, Botulinum toxin injections may help reduce headache frequency.
Bladder dysfunction: Botulinum toxin injections can also help reduce urinary incontinence caused by an overactive bladder.
Eye twitching: Botulinum toxin injections may help relieve contracture or twitching of muscles around the eye.
Risks:
Botox injections are relatively safe when performed by an experienced dermatologist in Delhi. Possible side effects include:
- Pain, swelling or bruising at the injection site.
- A headache or flu-like symptoms.
- Droopy eyelid or cockeyed eyebrows.
- Crooked smile or drooling.
- Eye dryness or excessive tearing.
Although very unlikely, it is possible for the effect of botulinum toxin to spread to other parts of the body and cause botulism-like signs and symptoms.
Call your doctor right away if you notice any of these effects hours to weeks after receiving Botox:
- Muscle weakness all over the body.
- Vision problems.
- Trouble speaking or swallowing.
- Trouble breathing.
- Loss of bladder control.
Doctors generally recommend against using Botox when you’ are pregnant or breastfeeding.

Select your doctor carefully:
Botox injections must be used only under a doctor’s care. It is important that injections be placed precisely in order to avoid side effects.
Botox injections therapy can be dangerous if it’s administered incorrectly. Ask for a referral from your primary care doctor.
Look for a skin specialist in Delhi who specializes in your condition and who has experience in administering Botox treatments.
A skilled and properly certified doctor can advise you on the procedure and help determine if it best suits your needs and health.
How you prepare:
Tell your doctor if you have received any type of botulinum toxin injections within the past four months.
And tell him or her if you take muscle relaxants, sleeping aids or allergy medications.
If you take blood thinners, You may need to forgo them for several days before your injection, to reduce your risk of bleeding or bruising.
What you can expect:
Before the procedure:
Most people tolerate the injection discomfort well.
But you may want your skin to be numbed beforehand, especially if your palms or soles are being treated for excessive sweating.
Your doctor might use one or more of various methods available to numb the area, such as topical anaesthesia, ice and vibration anaesthesia, which uses massage to reduce discomfort and effects.
During the procedure:
Your doctor uses a thin needle to inject botox injections tiny amounts of botulinum toxin into your skin or muscles.
The number of injections needed depends on many factors, including the extent of the area being treated. Botox injections are usually done in a doctor’s office.
After the procedure:
Expect to resume your normal daily activities right after the procedure. Take care, though, not to rub or massage the treated areas.
This can cause the toxin to migrate to a different area.
Results:
Botulinum toxin or botox injections usually begin working a few days after treatment. Depending on the problem being treated, the effect may last three months or longer.
To maintain the effect, you will need regular follow-up injections.






 WhatsApp us
WhatsApp us